Difference between revisions of "Amiga"
(→Range) |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
[[File:Amiga500 system.jpg|thumb|right|Amiga 500]] | [[File:Amiga500 system.jpg|thumb|right|Amiga 500]] | ||
[[File:Amiga 600.jpg|thumb|right|Amiga 600]] | [[File:Amiga 600.jpg|thumb|right|Amiga 600]] | ||
| + | [[File:Amiga 1200.jpg|thumb|right|Amiga 1200]] | ||
| + | [[File:Amiga A1000.jpg|thumb|right|Amiga 1000]] | ||
| + | [[File:Amiga 2000.gif|thumb|right|Amiga 2000]] | ||
| + | [[File:Amiga-3000T-compleet.jpg|thumb|right|Amiga 3000T-040]] | ||
[[File:Amiga CDTV.jpg|thumb|right|Amiga CDTV with all accessories]] | [[File:Amiga CDTV.jpg|thumb|right|Amiga CDTV with all accessories]] | ||
[[File:Amiga-CD32-wController-L-TRSP.png|thumb|right|Amiga CD32]] | [[File:Amiga-CD32-wController-L-TRSP.png|thumb|right|Amiga CD32]] | ||
| Line 10: | Line 13: | ||
Superficially similar to the [[Atari ST]], using the same [[Motorola 68000]] processor and similar memory and screen modes, but it had a lot of co-processor and sweet architecture tricks making it a powerful computer, with excellent sound hardware for its time. Many early releases were lazy conversions from the ST that did not fully exploit the above (rather like what the Amstrad suffered with Spectrum ports) but later releases largely did exploit the system. | Superficially similar to the [[Atari ST]], using the same [[Motorola 68000]] processor and similar memory and screen modes, but it had a lot of co-processor and sweet architecture tricks making it a powerful computer, with excellent sound hardware for its time. Many early releases were lazy conversions from the ST that did not fully exploit the above (rather like what the Amstrad suffered with Spectrum ports) but later releases largely did exploit the system. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Amiga had a revolutionary custom-built sound chip that didn't sound like any other computer of its era. What it sounds like is a Fairlight CMI synth - in other words, virtually anything you want. Waveforms are held in RAM and read out at various speeds. | ||
The A500 was perhaps the most well known emblematic model. Famous Amiga originals released for the CPC include [[Lemmings]], [[Defender of the Crown]], [[Sim City]], [[Shadow of the Beast]] and [[Pinball Dreams]]. | The A500 was perhaps the most well known emblematic model. Famous Amiga originals released for the CPC include [[Lemmings]], [[Defender of the Crown]], [[Sim City]], [[Shadow of the Beast]] and [[Pinball Dreams]]. | ||
| Line 33: | Line 38: | ||
*A4000 (1992): A replacement for the A3000, has the AGA chipset and either a 68030 or 68040 processor. In 1994 came the A4000T, an A4000 in a tower case. | *A4000 (1992): A replacement for the A3000, has the AGA chipset and either a 68030 or 68040 processor. In 1994 came the A4000T, an A4000 in a tower case. | ||
*CD32 (1993): Video game console marketed as the first 32-bit games console. It is essentially a keyboard-less A1200 home computer without the I/O ports, but with the addition of a CD-ROM drive and an improved version of the AGA chipset. It is the final hardware to be developed by Commodore. | *CD32 (1993): Video game console marketed as the first 32-bit games console. It is essentially a keyboard-less A1200 home computer without the I/O ports, but with the addition of a CD-ROM drive and an improved version of the AGA chipset. It is the final hardware to be developed by Commodore. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Commodore shut down the Amiga division on April 26, 1994, and filed for bankruptcy three days later. Commodore's assets were purchased by Escom, a German PC manufacturer, who created the subsidiary company Amiga Technologies. They re-released the A1200 and A4000T, and introduced a new 68060 version of the A4000T. But Escom went bankrupt in 1996. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Gateway, an American PC manufacturer, eventually acquired the Amiga brand and technology in 1997. Gateway was then working on a brand new Amiga platform. However this did not materialize and in 2000, Gateway sold the Amiga brand without having released any products. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 38: | Line 47: | ||
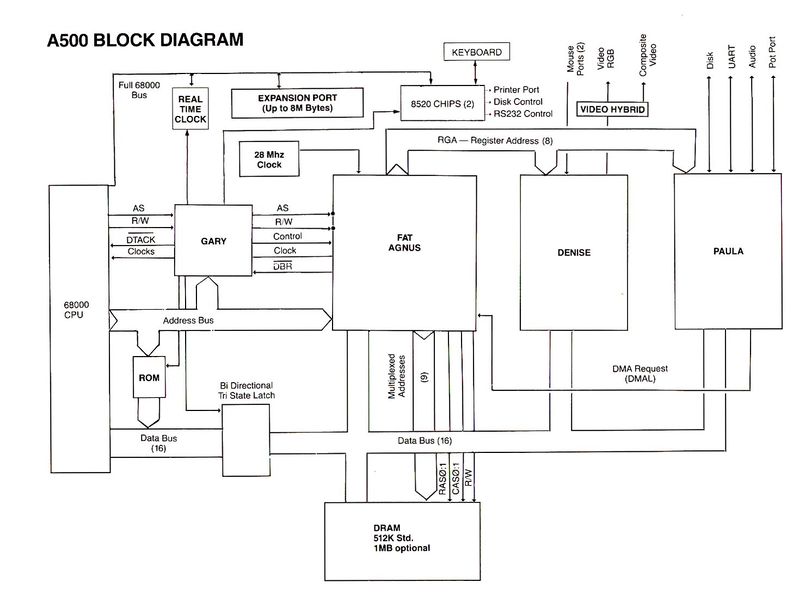
==Block Diagram== | ==Block Diagram== | ||
| − | [[File:A500-block-diagram.jpg| | + | [[File:A500-block-diagram.jpg|800px]] |
'''Agnus''' (Address GeNerator UnitS) is the core chip in the system, managing all access to chip RAM for the 68000 processor and other custom chips through a complex priority system. It includes the '''Blitter''', which enables fast memory data transfers without processor involvement, and the '''Copper''', a video-synchronized co-processor. | '''Agnus''' (Address GeNerator UnitS) is the core chip in the system, managing all access to chip RAM for the 68000 processor and other custom chips through a complex priority system. It includes the '''Blitter''', which enables fast memory data transfers without processor involvement, and the '''Copper''', a video-synchronized co-processor. | ||
| Line 56: | Line 65: | ||
*[https://grandis.nu/turran/ Turran FTP] | *[https://grandis.nu/turran/ Turran FTP] | ||
*[https://amiga.net.au/files/Tech_Amiga/Commodore_Amiga_500_Technical_Manual.pdf Amiga 500 Service Manual] | *[https://amiga.net.au/files/Tech_Amiga/Commodore_Amiga_500_Technical_Manual.pdf Amiga 500 Service Manual] | ||
| − | *[http://amigadev.elowar.com/read/ADCD_2.1/Hardware_Manual_guide/node0001.html Amiga Hardware Reference Manual] | + | *[http://amigadev.elowar.com/read/ADCD_2.1/Hardware_Manual_guide/node0001.html Amiga Hardware Reference Manual] [https://retro-commodore.eu/files/downloads/amigamanuals-xiik.net/Other/Amiga%20Hardware%20Reference%20Manual-ENG.pdf PDF version] |
*[https://eab.abime.net/ English Amiga Board] | *[https://eab.abime.net/ English Amiga Board] | ||
*[https://youtu.be/kjapiUQOi2s Commodore History - The Amiga 1000] by [[The 8-Bit Guy]] | *[https://youtu.be/kjapiUQOi2s Commodore History - The Amiga 1000] by [[The 8-Bit Guy]] | ||
*[https://youtu.be/ws3DJF7MbMU Part 1] [https://youtu.be/BcXcy2b1dRM Part 2] Amiga Story by [[Nostalgia Nerd]] | *[https://youtu.be/ws3DJF7MbMU Part 1] [https://youtu.be/BcXcy2b1dRM Part 2] Amiga Story by [[Nostalgia Nerd]] | ||
| − | *[https://youtu.be/wv4_3WLgyr0 | + | *[https://youtu.be/wv4_3WLgyr0 Amiga 1000] [https://youtu.be/I8D_ciE4zi0 Amiga 500] [https://youtu.be/qX7Ki0WkFxk Amiga 600] [https://youtu.be/-GGfu6_gEZs Amiga 3000] presented by [[Rodrik Studio]] |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
*[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wdUa20kUXM8&list=PLIX9fyYxV0k_NtBiHZtXs_UIccGTbnAjz PC vs Amiga] [https://youtu.be/fQU-WZZ67yM C64 SID vs Amiga Paula sound chip] | *[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wdUa20kUXM8&list=PLIX9fyYxV0k_NtBiHZtXs_UIccGTbnAjz PC vs Amiga] [https://youtu.be/fQU-WZZ67yM C64 SID vs Amiga Paula sound chip] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:35, 23 May 2025
Commodore's 16 bit home computer AMIGA is one of the best known and loved of its generation.
It was maybe the first real Multi Media home computer long before Apple's Mac.
Superficially similar to the Atari ST, using the same Motorola 68000 processor and similar memory and screen modes, but it had a lot of co-processor and sweet architecture tricks making it a powerful computer, with excellent sound hardware for its time. Many early releases were lazy conversions from the ST that did not fully exploit the above (rather like what the Amstrad suffered with Spectrum ports) but later releases largely did exploit the system.
The Amiga had a revolutionary custom-built sound chip that didn't sound like any other computer of its era. What it sounds like is a Fairlight CMI synth - in other words, virtually anything you want. Waveforms are held in RAM and read out at various speeds.
The A500 was perhaps the most well known emblematic model. Famous Amiga originals released for the CPC include Lemmings, Defender of the Crown, Sim City, Shadow of the Beast and Pinball Dreams.
Although it was great, it was eventually left behind by the PC standard thanks to Commodore's Corporates non sense and failure to develop the design further. The ECS chipset offered minimal improvements over the original, and even the AGA chipset was underwhelming. This is a kind of sweet vengeance for Amstrad users (who suffered the same thing, thank you Lord Sugar...).
Fun fact: the Amiga engineers left an hidden message in some Amigas, triggered by using some key combination, that said: "We made Amiga, They fucked it up". Source
4.85 million units sold.
Range
- A1000 (1985): Technically an avant-gardiste multimedia PC. Has the OCS chipset.
- A500 (1987): The first mass-market Amiga model, the most successful, and the one the most games were designed around. The case is the Combo style shared with Atari ST or even Amstrad Plus range. All but the latest models use the OCS chipset
- A2000 (1987): Like the A1000, a PC style professionnal machine. In 1990, Commodore UK sold the A1500, a variant of the A2000 with 2 floppy drives and no hard drive. Like the A1500, the A2500 is not a distinct model but an A2000 equipped with a 68020 or 68030 accelerator card.
- A3000 (1990): A workstation system aimed at productivity users, using a 68030 processor and the new Kickstart 2 and Workbench 2. In 1991 came the A3000T, an A3000 in a tower case.
- CDTV (1991): Home multimedia entertainment and video game console. It is essentially an A500 home computer with a CD-ROM drive and remote control. With optional keyboard, mouse, and floppy disk drive, it gained the functionality of the regular Amiga.
- A500+ (1991): Features the updated Kickstart 2 and Workbench 2, 1MB internal memory and the ECS (Enhanced Chip Set).
- A600 (1992): a compact A500 with no numeric keypad, looks a lot like the newer C64 (not the bread bin ones). Similar internal hardware to the A500+, though with space for an internal hard drive.
- A1200 (1992): Intended as a long-term replacement for the A500, with 2MB memory and the new AGA chipset.
- A4000 (1992): A replacement for the A3000, has the AGA chipset and either a 68030 or 68040 processor. In 1994 came the A4000T, an A4000 in a tower case.
- CD32 (1993): Video game console marketed as the first 32-bit games console. It is essentially a keyboard-less A1200 home computer without the I/O ports, but with the addition of a CD-ROM drive and an improved version of the AGA chipset. It is the final hardware to be developed by Commodore.
Commodore shut down the Amiga division on April 26, 1994, and filed for bankruptcy three days later. Commodore's assets were purchased by Escom, a German PC manufacturer, who created the subsidiary company Amiga Technologies. They re-released the A1200 and A4000T, and introduced a new 68060 version of the A4000T. But Escom went bankrupt in 1996.
Gateway, an American PC manufacturer, eventually acquired the Amiga brand and technology in 1997. Gateway was then working on a brand new Amiga platform. However this did not materialize and in 2000, Gateway sold the Amiga brand without having released any products.
Block Diagram
Agnus (Address GeNerator UnitS) is the core chip in the system, managing all access to chip RAM for the 68000 processor and other custom chips through a complex priority system. It includes the Blitter, which enables fast memory data transfers without processor involvement, and the Copper, a video-synchronized co-processor.
Denise (Display ENabler) serves as the primary video processor, handling a display of 320 or 640 pixels wide by 200 (NTSC) or 256 (PAL) pixels tall without overscan. It supports interlacing for doubled vertical resolution, though this causes flickering on older monitors. Denise uses planar bitmap graphics with one to five bitplanes for 2 to 32 colors from a 4096-color palette, plus a sixth bitplane for special modes like Halfbrite and Hold-And-Modify (HAM). It also manages eight sprites, single-pixel scrolling, "dual-playfield" mode, and processes mouse and digital joystick inputs.
Paula (Ports, Audio, Uart and Logic) is the audio chip, featuring four hardware-mixed 8-bit PCM sound channels and sample rates up to 28kHz. Beyond audio, Paula manages interrupts, floppy disk drive, serial port, and analog joystick inputs, along with other I/O tasks.
Links
- Amiga at the English-language Wikipedia
- AmigaWiki
- The iconic "Only Amiga makes it possible" promo video Amiga Commercials
- All Commodore Amiga games Over 100 Amiga games in under 1 hour Over 100 Amiga AGA games in under 1 hour
- Amiga 500 Archive
- Turran FTP
- Amiga 500 Service Manual
- Amiga Hardware Reference Manual PDF version
- English Amiga Board
- Commodore History - The Amiga 1000 by The 8-Bit Guy
- Part 1 Part 2 Amiga Story by Nostalgia Nerd
- Amiga 1000 Amiga 500 Amiga 600 Amiga 3000 presented by Rodrik Studio
- PC vs Amiga C64 SID vs Amiga Paula sound chip